HYDROCARBON BIOREMEDIATION
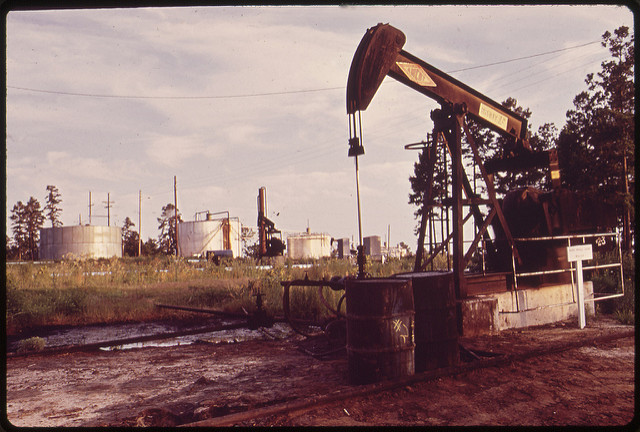

| Oil Spills - As long as the microbes can reach the hydrocarbon contaminants with the necessary oxygen, nutrients, moisture, and the temperature and pH are within the microbes working range, then remediation will be successful. |
Successful Bioaugmentation with Microbes |
||
|
Bioremediation of hydrocarbons is best accomplished with a process called Bio-augmentation. That is, the addition of a large number of selected, laboratory grown, standardized microorganisms to a contaminated matrix. These contaminant specific microbes capable of degrading these hydrocarbon compounds breaking them down into carbon dioxide and water. The microbes will survive and consume their contaminant food source until the unwanted pollutant is remediated. This is possible because the microbes use parts of the hydrocarbons to maintain their own metabolic process Bioaugmentation can be used for in-situ and ex-situ soil and water remediation. It can be used in conjunction with traditional mechanical methods or on its own. Microbial bioaugmentation is most successful in treating the residual biofilms in the soil. The primary objective of bioremediation is to provide the microbes with an environment that is optimum for their survival and reproduction, and in doing so you maximize the effectiveness of the bioreclamation. Bioaugmentation and Bioremediation of oil spills with microbes requires a few criteria to be successful.
Frequently Asked Questions about Hydrocarbons and Bioremediation |
|
Hydrocarbon remediation Hydrocarbon FAQ's Landfarming MIcrobes Product Info